Table Of Content
In the PROactive cohort study the research assessment is an integrated part of clinical care. Children are included when they visit the outpatient clinic and are followed up annually. Cohort design is a type of nonexperimental or observational study design. In a cohort study, the participants do not have the outcome of interest to begin with. They are then followed over time to evaluate for the occurrence of the outcome of interest. Some examples of cohort studies are (1) Framingham Cohort study, (2) Swiss HIV Cohort study, and (3) The Danish Cohort study of psoriasis and depression.
Body weight in neurological and psychiatric disorders: a large prospective cohort study - Nature.com
Body weight in neurological and psychiatric disorders: a large prospective cohort study.
Posted: Thu, 04 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
University of Houston
Inclusion can take place between 2 and 18 years of age, depending on the moment of diagnosis. Besides children with a chronic condition, children with unexplained medical symptoms are included in the PROactive cohort study. These advantages and disadvantagesare common to all retrospective studies. It was a longitudinal study of HIV-infected individuals to conduct research on HIV pathogenesis, treatment, immunology, and coinfections.
Data collection PROMs
This effort resulted in a database of separate name lists for Chinese, Filipinos, Japanese-Americans, Native Hawaiians, Koreans, Latinos, and Samoans. Because some names fell into more than one list (e.g., Lee could be Chinese, Korean, or White), these lists were not mutually exclusive. In addition, the voters' registration file in Hawaii has a special identification field for persons of Native Hawaiian ancestry. From 2017 to 2020, children in the first year after treatment for childhood cancer were also assessed as part of this cohort study. The PROactive cohort study has a continuous longitudinal design and includes children with a chronic condition in a broad age range.
Temple University
In the initial set-up of this cohort, we did not yet succeed to guarantee this long-term follow-up due to the fact that children are seen in a different hospital by different physicians than adults and we wanted to guarantee a direct feedback loop in clinical care. Currently, children are followed until 18 years of age, although follow-up into adulthood, including transition, is under development and the first inclusions will start soon. While the biopsychosocial model tells us what factors can be considered when assessing children with a chronic disease, it does not outline how these factors relate to the child’s outcome over time. The cognitive behavioural model to explain symptoms, such as fatigue, distinguishes predisposing, precipitating, and perpetuating factors.
This type of study is feasible if an investigator has access to a dataset that fits the research question. The dataset must also have adequate measurements about the predictor variables. Table 5 shows the proportion of subjects who engage in more than 3 hours per week of vigorous physical activity (strenuous sports or vigorous work).
Relative risks of 1.5 or lower will be detectable in all four groups for prostate and breast cancers, while risks of 1.9 or lower will be detectable for colorectal cancer and 2.0 or lower for lung cancer. PROactive cohort study aims to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in the field of data collection in children. The Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System[36] (PROMIS®) is an upcoming development. PROMIS allows for a reduction in the number of questions, which should reduce completion time in the majority of the PROactive patients, while maintaining determinants and outcome measures. The PROactive study team is closely following these developments and aiming to implement them where possible. To achieve a true life cycle perspective, it is important to follow-up patients above the age of 18.
Data collection, editing, and management
Twice a year, data extraction of pre-selected biological variables takes place. If there are several moments of clinical assessments, the data entry closest to filling out the PROMs is chosen. If large electronic health care databases exist, as they do, e.g., in the Scandinaviancountries and the USA, a very large cohort, with tens or hundreds of thousands of subjects,can quickly be identified and followed up in the database. Information on the variables ofinterest can be extracted in a relatively short period of time with little effort andexpense.
Transitional Youth Mobilizing for Change (TYM4Change)
Gathered information about the causes of health problems that affect Black women. Julia Simkus is a graduate of Princeton University with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology. She is currently studying for a Master's Degree in Counseling for Mental Health and Wellness in September 2023. Let us assume that all the cardiovascular events occurred at the end of the 2nd year. They can be more time-consuming than other options, such as cross-sectional or case-control studies. While there is some risk involved in drug trials too, scientists only test drugs on humans when they are reasonably sure they are beneficial and when participants are fully aware of the risk.
The natural or incidental exposure to these risk factors (e.g. time spent in the sun), or self-administered exposure (e.g. smoking), can be measured without subjecting participants to risk factors outside of their individual lifestyles, habits, and choices. An important consideration is that PROactive cohort study now aims to include children only after the diagnostic phase. Even so, it may be even better to start measuring children from the moment they receive the diagnosis.
It is important that we include only patients with permanent addresses in the area for long-term cohort studies. Details about the stay (permanent address, temporary address, and duration of residence in the current address) should be a part of the inclusion criteria. Sometimes, the direction may not be as well defined as prospective and retrospective. One may analyze retrospective data on a group of people well as collect prospective data from the same individuals. It is difficult to use RCTs to determine the causes and risk factors for disease because this would involve intentionally exposing participants to something that could make them ill. The study has made important contributions to the understanding of heart health.
After the family completes the assessments, the raw results scores (with traffic light colours), the scores in a chart with threshold and a written summary become visible in the EHR. Retrospective cohort studies have their own benefits, namely that they can be conducted relatively quickly, easily, and cheaply than other types of research. Researched long-term effects of nurses” nutrition, hormones, environment, and work-life on health and disease development. Cohort studies can be very useful for evaluating the effects and risks of rare diseases or unusual exposures, such as toxic chemicals or adverse effects of drugs. Other methods such as logistic regression, Kalpan–Meier curves, cox-regression, Poisson regression, lognormal regression may be useful in cohort studies.
There is growing recognition of the importance of physical activity in relation to cancer risk. Interestingly, African-American and Japanese-American men and women have the lowest levels of vigorous physical activity (table 5) and the highest rates of colorectal cancer (table 1). Physical activity has been convincingly related to a lower colon cancer risk (59), although no particular type of activity has yet been established as most beneficial.
Fish consumption is highest among the Japanese-Americans and Native Hawaiians. Whites and Latinos have high intakes of dairy products, especially compared with the Japanese-Americans. Intake of legumes is much higher among the Latinos than any other group, although tofu is consumed most by the Japanese-Americans. Latinos are the lowest consumers of green and cruciferous vegetables, whereas they (together with Native Hawaiians) are the highest consumers of yellow-orange and allium vegetables. To develop emerging Latinx leaders in Stanislaus County through youth-led collective action efforts, building youth power and skills to connect networks for policy change.
In education, the word cohort is used to refer to a group of students who have been grouped together based on some category, such as grade level or graduation year. In this context, cohort is often used when other words like class might not be entirely precise. For example, a class of students may be divided into multiple cohorts, such as when the teacher spends time teaching each one separately.
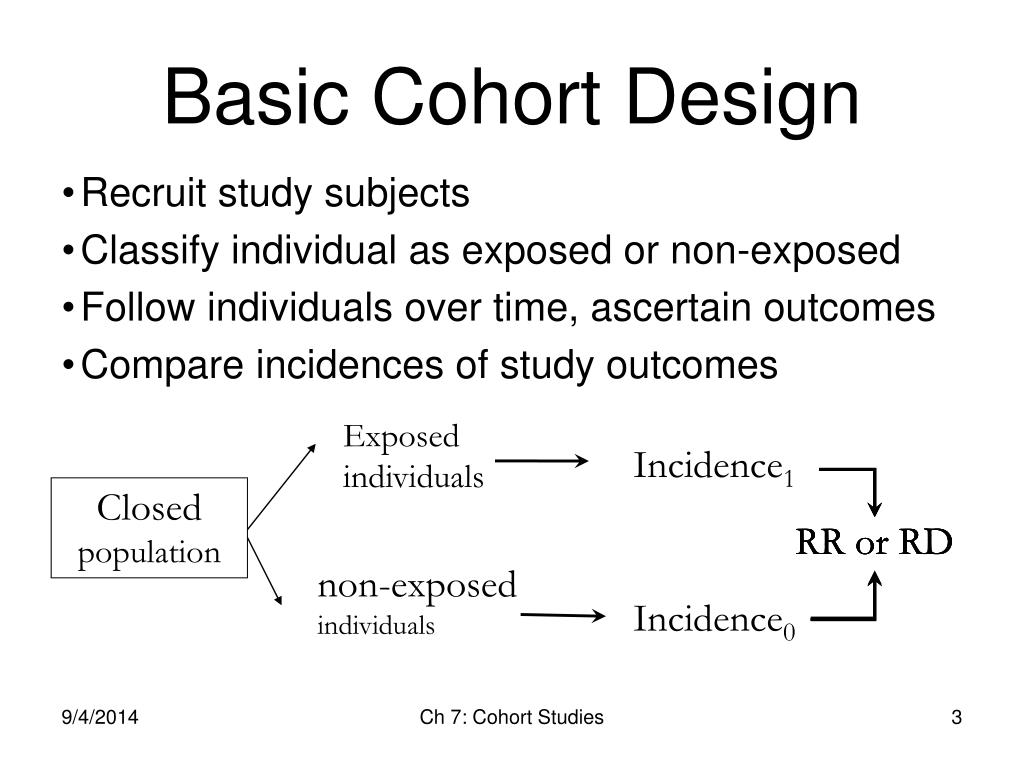
It is important the exposure, outcome, and other variables should be measured similarly in both the study and the comparison group. As seen in Figure 1, at baseline, some of the study participants have exposure (defined as exposed) and others do not have the exposure (defined as unexposed). Over the period of follow-up, some of the exposed individuals will develop the outcome and some unexposed individuals will develop the outcome of interest. Thus, some of the participants may have the exposure and others do not have the exposure at the time of initiation of the study. Another example of a long-running cohort study is the Framingham Heart Study.

No comments:
Post a Comment